Understanding Edge Computing: A New Era for Enterprise Applications
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce latency, and enhance user experiences. One technology that has emerged as a game-changer in this quest is edge computing. But what exactly is edge computing, and how does it revolutionize enterprise applications? Let's dive deep into this fascinating subject.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that processes data closer to the source of data generation rather than relying on a centralized data center. This means that instead of sending all data to a distant server for processing, edge computing allows for data to be processed at the "edge" of the network, near the devices that generate it. This approach helps to minimize latency and bandwidth usage.
Why the Shift to Edge Computing?
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, the amount of data generated is skyrocketing. Traditional cloud computing models struggle to keep up with this demand, leading to delays and inefficiencies. Edge computing addresses these challenges by:
- Reducing Latency: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing significantly decreases the time it takes for data to travel to a server and back.
- Enhancing Bandwidth Efficiency: Instead of sending large volumes of data back to the cloud, only the most critical information is transmitted, saving bandwidth.
- Improving Reliability: Edge computing can operate independently of cloud services, ensuring that critical applications continue to function even during network outages.
How Edge Computing Works
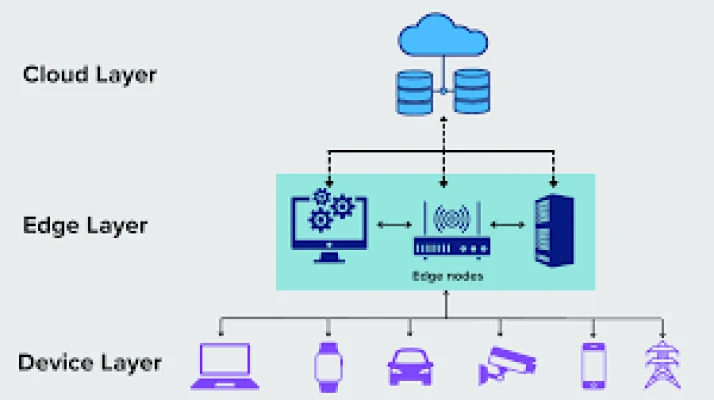
To understand edge computing, it's helpful to visualize it as a series of layers. At the bottom layer are the devices that generate data—think smart sensors, cameras, and IoT devices. The next layer is the edge devices, which are responsible for processing and analyzing the data. Finally, the top layer consists of cloud services, which can be used for additional processing or storage if needed.
Components of Edge Computing
There are several key components that make edge computing effective:
- Edge Devices: These are the actual devices that collect data, such as sensors in manufacturing equipment or cameras in smart cities.
- Edge Gateways: These serve as intermediaries, collecting data from multiple devices and processing it before sending it to the cloud.
- Edge Servers: These perform more complex computations locally, allowing for real-time data analysis.
- Cloud Services: Although edge computing processes data locally, cloud services still play a role in storing data and conducting deep analytics when necessary.
Benefits of Edge Computing for Enterprises
So, why should enterprises consider adopting edge computing? Here are some compelling benefits:
1. Faster Decision Making
In industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and finance, making quick decisions can mean the difference between success and failure. Edge computing enables real-time data analysis, allowing businesses to respond to issues instantly. For example, a manufacturing plant can monitor equipment performance in real-time and make adjustments on the fly, preventing costly downtime.
2. Enhanced Security
Data security is a top concern for enterprises. By processing data at the edge, sensitive information can be kept closer to its source, reducing the risk of exposure during transmission. Additionally, edge computing can incorporate advanced security measures directly at the device level, adding another layer of protection.
3. Cost Savings
Reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to and from the cloud can lead to significant cost savings. Companies can save on bandwidth and storage costs while also improving operational efficiency. For instance, a smart city could use edge computing to manage traffic lights based on real-time data, optimizing traffic flow without relying heavily on cloud resources.
4. Scalability
As businesses grow, so do their data needs. Edge computing allows enterprises to scale their operations without a complete overhaul of their infrastructure. Adding new edge devices can be done seamlessly, accommodating increased data loads without overwhelming centralized systems.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Let’s explore how various industries are leveraging edge computing:
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, edge computing can facilitate remote patient monitoring. Devices can analyze patient data in real-time and send alerts to healthcare providers if any abnormalities are detected. This not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the need for hospital visits.
2. Retail
Retailers can use edge computing to analyze customer behavior in real-time. By processing data from in-store sensors, retailers can optimize inventory management and personalize customer experiences, leading to higher sales.
3. Smart Cities
Edge computing enables smart cities to manage resources efficiently. For example, traffic management systems can analyze traffic patterns in real-time and adjust traffic signals accordingly, reducing congestion and improving air quality.
Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Enterprises need to consider:
- Integration Complexity: Integrating edge computing with existing systems can be complex and require significant investment.
- Data Management: Managing data across multiple edge devices can become cumbersome, requiring robust data governance strategies.
- Security Risks: While edge computing can enhance security, it also opens up new vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
Conclusion: The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is poised to transform the way enterprises operate by enabling real-time data processing, improving efficiency, and enhancing security. As technology continues to evolve, businesses that embrace edge computing will be better equipped to meet the demands of a data-driven world. Whether you're in healthcare, retail, or manufacturing, considering edge computing could be the key to staying ahead of the competition.
In summary, edge computing is more than just a trend; it’s a necessary evolution in how we handle data. By bringing enterprise applications closer to the source of data, businesses can unlock a world of possibilities. Are you ready to take the leap into the future of computing?