API Architecture: REST vs GraphQL
In the world of software development, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are essential. They allow different software applications to communicate with each other. Two popular API architectures that developers often discuss are REST (Representational State Transfer) and GraphQL. Each has its strengths and weaknesses. In this blog post, we will dive deep into both REST and GraphQL, comparing their features, advantages, and use cases.
Understanding REST
What is REST?
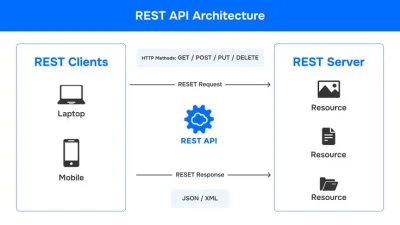
REST is an architectural style that uses standard HTTP methods to manage data. It relies on stateless communication and is resource-based, which means it treats data as resources that can be created, read, updated, or deleted (CRUD operations). REST APIs are designed around resources, which are identified by URLs.
Key Features of REST
- Stateless: Each request from a client to a server must contain all the information needed to understand and process the request. The server does not store any client context.
- Resource-Based: Every resource is identified by a unique URL, making it easy to access specific data.
- Standard HTTP Methods: REST uses standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE to perform operations on resources.
- Cacheable: Responses can be cached to improve performance, which is a significant advantage for frequently accessed data.
Understanding GraphQL
What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for executing those queries by using a type system you define for your data. Developed by Facebook, GraphQL allows clients to request exactly the data they need, avoiding over-fetching or under-fetching data.
Key Features of GraphQL
- Flexible Queries: Clients can specify exactly what data they need in a single request, reducing the number of requests made to the server.
- Strongly Typed Schema: GraphQL uses a schema to define the types of data and their relationships, making it easier to understand and maintain.
- Single Endpoint: Unlike REST, which often has multiple endpoints for different resources, GraphQL typically exposes a single endpoint for all requests.
- Real-Time Data: GraphQL supports subscriptions, allowing clients to receive real-time updates when data changes.
Comparing REST and GraphQL
1. Data Fetching
One of the most significant differences between REST and GraphQL is how data is fetched.
- REST: In REST, you may need to make multiple requests to different endpoints to gather all the required data. For example, if you want user information and their posts, you would need to fetch from two different endpoints.
- GraphQL: With GraphQL, you can fetch all the required data in a single request. You can structure your query to get user information along with their posts in one go.
2. Versioning
Versioning is a common challenge in API development.
- REST: When changes are made to the API, a new version may need to be released (e.g., v1, v2). This can lead to confusion and maintenance overhead.
- GraphQL: GraphQL APIs typically avoid versioning. Instead of creating new versions, you can add new fields and types to the schema without affecting existing queries.
3. Performance
Performance can vary greatly between REST and GraphQL depending on the use case.
- REST: REST APIs can be fast for simple data retrieval but may become slow when multiple requests are needed, leading to increased latency.
- GraphQL: GraphQL can improve performance by reducing the number of requests made. However, complex queries may lead to performance issues if not managed properly.
4. Caching
Caching is vital for improving the speed of an API.
- REST: REST APIs can leverage HTTP caching, which can be very effective. Responses can be cached based on the URL, improving performance for frequently accessed resources.
- GraphQL: Caching can be more complex with GraphQL since there is typically only one endpoint. Developers need to implement custom caching strategies to optimize performance.
When to Use REST and When to Use GraphQL
Use Cases for REST
REST is a great choice when:
- You have a simple application with straightforward data retrieval needs.
- You want to leverage HTTP caching for performance.
- You prefer a stateless architecture that is easy to scale.
Use Cases for GraphQL
GraphQL shines in scenarios where:
- You need to fetch complex, related data in a single request.
- You expect the API to evolve frequently and want to avoid versioning issues.
- You require real-time data updates through subscriptions.
Conclusion
Both REST and GraphQL have their unique advantages and challenges. The choice between them often depends on your specific use case, the complexity of your data, and your team's expertise. Understanding the differences between these two architectures will help you make an informed decision that best suits your project's needs.
As a developer, it’s essential to stay updated with the latest trends and technologies. Whether you choose REST or GraphQL, what matters most is how effectively you can meet your application's requirements while ensuring a great user experience.